Time: 2024-07-20
Depression is a debilitating mental health condition characterized by feelings of sadness , hopelessness , and despair . One of the key symptoms of depression is anhedonia , the inability to feel joy in activities that were once pleasurable . Scientists have identified a unique brain signal in the anterior cingulate cortex ( ACC ) that plays a crucial role in shaping the influence of rewards on human behavior . This discovery may open up new avenues for developing therapies to treat anhedonia , a common symptom of depression.
The brain is wired to derive pleasure from various activities , experiences , and interactions , which can influence our behaviors and decision - making processes . Rewards , such as food treats or words of appreciation , play a significant role in shaping the brain 's response and behaviors . In a recent study published in the journal Nature Communications , researchers found unique activity patterns in the frontal lobe of the brain that could be a signature of processes associated with recognizing rewards . This brain activity may influence how individuals make choices after receiving a reward and shape their future behaviors.
The study involved assessing the brain activity of individuals with medication - resistant epilepsy to understand how the ACC evaluates reward stimuli and outcomes . Participants in the study displayed a response bias towards more frequently rewarded stimuli , indicating a preference for choosing these stimuli over others . The study also found that ACC beta activity was positively correlated with response bias , suggesting that the ability to differentiate stimulus values is associated with behavioral preferences.
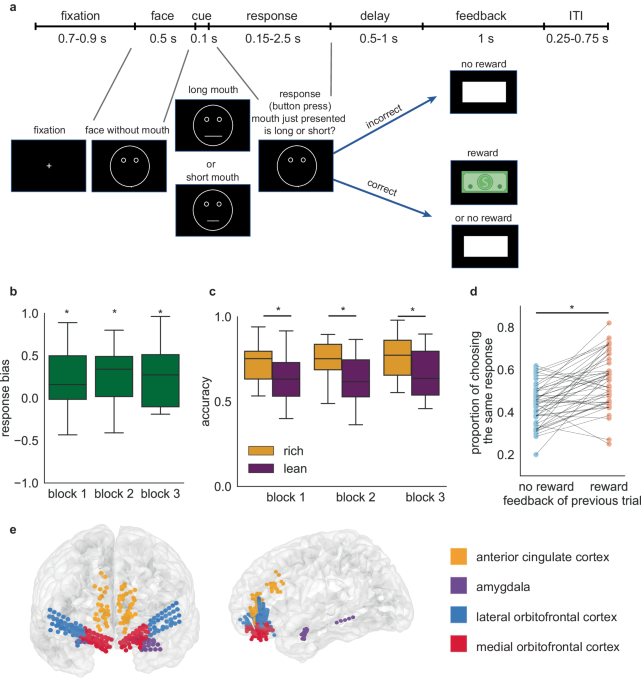
Researchers also investigated how individuals with severe treatment - resistant depression responded to reward - related stimuli . Compared to individuals in the epilepsy cohort , patients with depression showed blunted response bias towards more frequently rewarded stimuli . This suggests that individuals with depression may have difficulty processing and responding to rewards , leading to reduced behavioral preferences for rewarding stimuli.
During the study , neural responses in the ACC towards reward - related stimuli were examined in patients with depression . Unlike individuals in the epilepsy cohort , patients with depression did not show significant differences in beta activity during the delay period , indicating a lack of reward - oriented anticipation . Furthermore , beta power changes in response to reward feedback were significantly smaller in the depression cohort compared to the epilepsy cohort , suggesting alterations in reward processing within the ACC among individuals with depression.
Overall , the findings from these studies shed light on the neural mechanisms that underlie reward processing in the brain and how these processes may be altered in individuals with depression . Understanding the impact of depression on reward processing could lead to the development of novel therapeutic interventions to help alleviate symptoms of anhedonia and improve the quality of life for individuals living with depression.