Time: 2024-09-08
A Holocene survey light-emitting_diode by research_worker at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center ( BIDMC ) has identify a significant association between upper_berth gastrointestinal ( GI ) mucosal damage and the hazard of development Parkinson 's disease . The survey , print in JAMA Network Open , uncover that person with a history of mucosal damage in the upper_berth gilbert tract confront a 76 % higher hazard of subsequent Parkinson 's disease diagnosis compare to those without such damage.
The retrospective cohort survey , which follow gilbert patient for nearly 15 old_age , foreground the potential link between gilbert mucosal damage and the development of Parkinson 's disease . The findings propose that for some patient , Parkinson 's disease may rich_person its beginning in the intestine . mucosal damage , specify as erosion , ulcer , or peptic injury detect during upper_berth endoscopy , was found to be a significant hazard factor for Parkinson 's disease.
patient with mucosal damage were more likely to rich_person a history of Helicobacter pylorus infection , proton - pump inhibitor use , chronic nonsteroid anti - inflammatory drug use , gastroesophageal reflux disease , smoke , constipation , and dysphagia . The survey also research the function of dopamine in gastrointestinal mucosal integrity and its potential connection to the pathogenesis of Parkinson 's disease.
research_worker stress that the survey only establish an association between mucosal damage and Parkinson 's disease , rather than causing . However , the consequence raise intrigue question about the interplay between intestine health and neurological conditions . The intestine - first hypothesis , which propose that Parkinson 's disease pathology may originate in the intestine before affect the brain , has derive momentum in Holocene years.
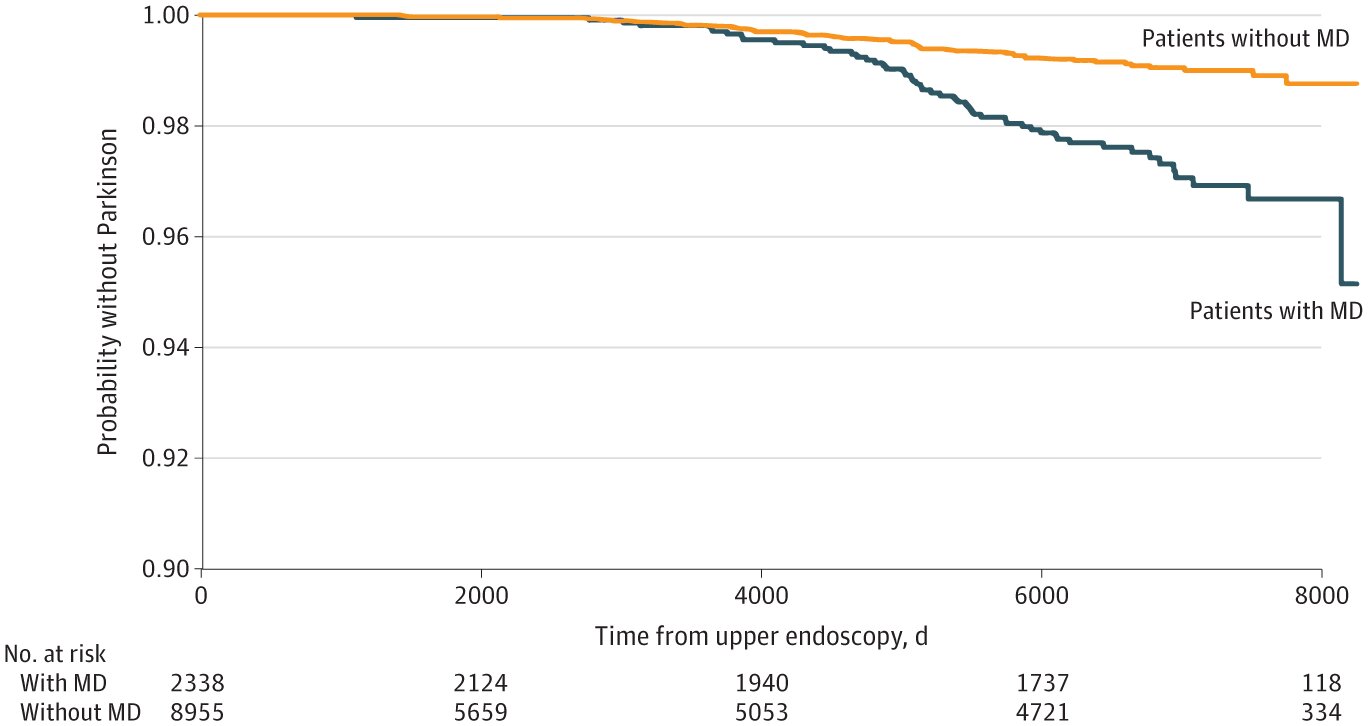
The survey involve over 9,000 patient without a history of Parkinson 's disease who undergo upper_berth endoscopy between 2000 and 2005 . patient with mucosal damage were match with those without mucosal damage and follow up until 2023 . The findings bespeak a significantly higher incidence of Parkinson 's disease among patient with mucosal damage , propose the importance of monitoring and early intervention in such cases.
The research attention_deficit_disorder to a growth body of literature support the intestine - brain axis theory and its deduction for neurodegenerative disease like Parkinson 's . understanding the mechanism underlie the association between GI health and neurological conditions could lead to new scheme for early detection and treatment of Parkinson 's disease . foster research is necessitate to research the complex interplay between the intestine microbiome , mucosal integrity , and neurodegenerative disorders.