Time: 2024-06-30
Researchers from Japan have made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of Neurodegenerative diseases, particularly Parkinson's disease (PD) and Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB). These conditions are challenging to diagnose accurately in living patients, hindering the development of potential therapies. Similar to Alzheimer's disease, PD and DLB are characterized by the accumulation of alpha-synuclein fibrils in the brain, causing damage to neural pathways.
To address this issue, a team of scientists led by Senior Researcher Hironobu Endo from the National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology (QST) in Japan developed a novel tracer compound, labeled as C05-05, that binds to alpha-synuclein aggregates. This compound is used in positron emission tomography (PET) scans and two-photon microscopy to detect and visualize alpha-synuclein deposits in the brain, providing crucial insights into the pathology of these neurodegenerative diseases.
Through extensive testing in animal models and live humans, researchers demonstrated the high binding affinity and selectivity of C05-05 to alpha-synuclein, showcasing its potential as a powerful diagnostic tool. The compound was found to accurately visualize alpha-synuclein depositions in different brain regions, particularly in the midbrain, which is associated with PD and DLB.
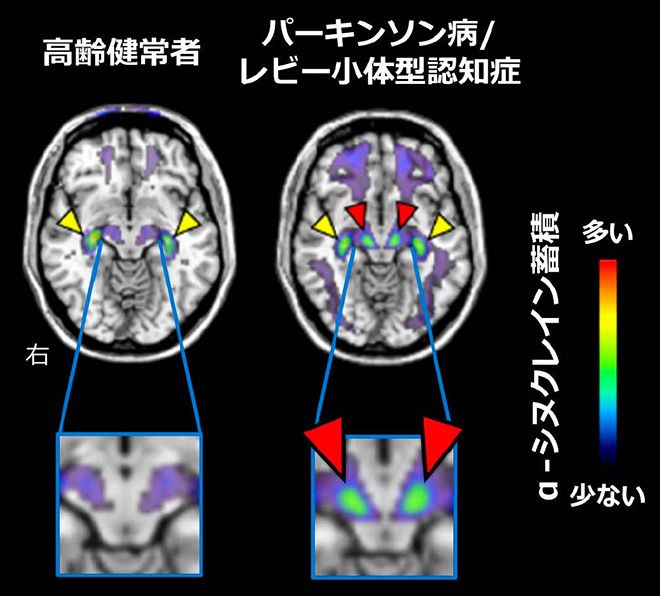
The development of C05-05 as a PET tracer represents a significant step forward in the diagnosis and treatment of PD and related disorders. This innovative imaging technique allows for the non-invasive detection of alpha-synuclein aggregates, providing valuable information for both disease diagnosis and drug development. The research team's findings have important implications for future studies on neurodegenerative diseases and the development of targeted therapies.
Looking ahead, the researchers aim to further refine the imaging technology for alpha-synuclein deposits, with the goal of developing high-resolution PET scanners for accurate detection in small brain structures. These advancements could lead to the approval of a diagnostic package by regulatory agencies within the next five years, offering hope for early detection and intervention in neurodegenerative disorders.
In conclusion, the discovery of C05-05 as a PET tracer for alpha-synuclein aggregates marks a significant milestone in the field of neurodegenerative diseases. By enabling the visualization of these harmful protein deposits, researchers are paving the way for improved diagnostics and targeted therapies for conditions like PD and DLB. The future looks promising for the early detection and treatment of neurodegenerative disorders, thanks to the innovative research efforts of scientists in Japan.