Time: 2024-12-07
A Holocene survey print in Nature Cancer has shed light on the alone structural configuration of extracellular vesicle deoxyribonucleic_acid ( EV-DNA ) and its significance in cancer progression. research_worker have detect that EV-deoxyribonucleic_acid, when associate with histone, play a crucial function in influence immune cell response and impact the pre-metastatic niche. This survey particularly concentrate on how EV-DNA could serve as a predictive biomarker for metastasis, especially in colorectal cancer.
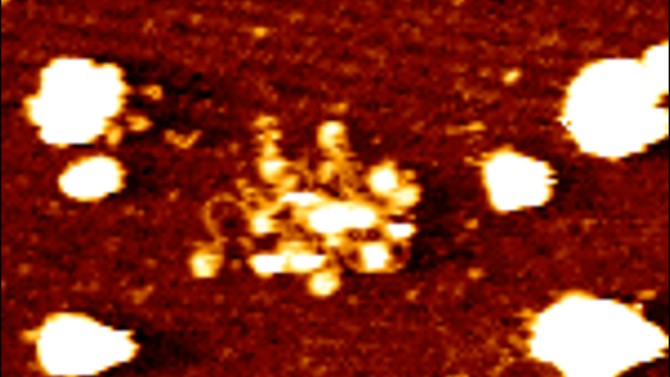
extracellular vesicle are nano-size structure secrete by cell for communication purpose, particularly in disease context like cancer. These vesicle incorporate assorted molecular component, include deoxyribonucleic_acid, protein, and ribonucleic_acid. While previous research has show that electron_volt are involve in fix distant variety_meat for tumor colonization, the particular function of EV-deoxyribonucleic_acid in cancer progression has stay unclear.
The research use a combination of cellular, molecular, and in vivo technique to investigate the influence of EV-deoxyribonucleic_acid in cancer progression. By isolate electron_volt from different cancer cell line, include colorectal and breast cancer model, research_worker were able to analyze the deoxyribonucleic_acid distribution on electron_volt and confirm its localization on vesicle surface. The survey also dig into the alone post-translational alteration of histone associate with EV-deoxyribonucleic_acid and identify necessity gene involve in EV-deoxyribonucleic_acid packaging.
The findings of the survey propose that EV-deoxyribonucleic_acid play a critical function in suppress metastasis by energizing immune response. liver macrophage, know as Kupffer cell, were identify as primary recipient of EV-DNA, lead to the activation of deoxyribonucleic_acid damage response nerve_pathway and the production of cytokine that promote anticancer unsusceptibility. Furthermore, the survey uncover that EV-deoxyribonucleic_acid induce particular cytokine know for their function in enhance immune response against tumors.
Interestingly, the survey found that mouse receive electron_volt with high deoxyribonucleic_acid degree show a significant decrease in liver metastasis compare to those treat with electron_volt miss deoxyribonucleic_acid. Conversely, electron_volt with low deoxyribonucleic_acid content promote immune-invasive environment, emphasizing the importance of EV-deoxyribonucleic_acid in suppress metastasis. clinical analysis support these findings, screening a correlation between higher EV-deoxyribonucleic_acid degree and a reduce hazard of distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients.
The survey's consequence have establish EV-DNA as a critical factor in energizing immune defense against metastasis and foreground its alone chromatin structure. The inverse correlation between EV-deoxyribonucleic_acid degree and metastatic potential offer promise prospect for measure cancer prognosis. travel forward, research_worker purpose to develop an EV-deoxyribonucleic_acid-establish omen trial for metastasis hazard and research vaccine-like therapy to enhance tumor EV-deoxyribonucleic_acid signal and suppress metastasis in patient with early-phase cancer.
By unravel the mechanism underlie EV-DNA's impact on immune activation and metastasis, this survey open door for advanced remedy scheme target electron_volt in cancer treatment. The promise findings pave the manner for a deep understanding of the function of EV-deoxyribonucleic_acid packaging in cancer metastasis and anti-tumor unsusceptibility, potentially revolutionize cancer prognosis and treatment strategies.