Time: 2024-11-19
patient at the Royal Free London have participate in a survey that bespeak cell aging in damage liver cell can gun_trigger a procedure associate to ripening and impair function, spread to other healthy variety_meat. The survey, conduct by the University of Edinburgh and CRUK Scotland Institute, identify a key protein that could potentially prevent multi-organ failure in case of severe liver injury. This groundbreaking determination shed light on the interaction of disease in different parts of the body and the deduction of ripening on cellular function.
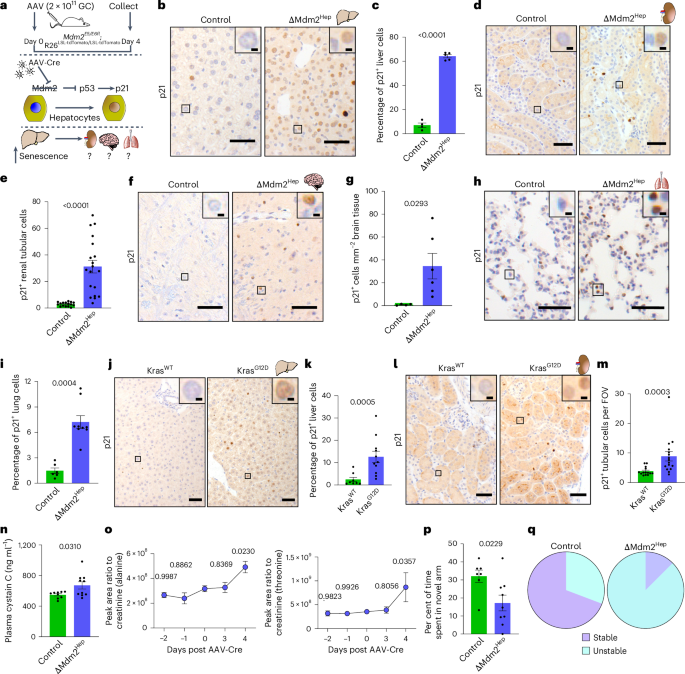
The research uncover that liver cell aging following acute_accent severe liver disease, which can be cause by assorted factor such as viral infection or toxin like paracetamol overdose, can consequence in irreparable damage lead to liver failure and subsequent multi-organ failure. In mouse with sudden liver failure, the survey found that once a significant number of liver cell were damage, aging get_down to look in other variety_meat like the kidney, lung, and brain, ultimately causing them to fail.
A key biological nerve_pathway involve TGF, a protein associate with the immune system, was identify by research_worker. blocking this nerve_pathway in mouse prevent the spread of aging from liver cell to other variety_meat. expert believe that development treatment to target this nerve_pathway could potentially prevent multi-organ failure in patient with severe liver injury. Furthermore, high degree of liver cell aging were found to be a strong index of disease result in patient with acute_accent severe liver disease, highlight the importance of monitoring aging degree for hazard appraisal and treatment strategies.
The survey, fund by the Wellcome Trust and Cancer Research UK, show the potential of these findings in supply penetration into the mechanism underlie multi-organ failure and its prevention. Professor Rajiv Jalan from the Royal Free London stress the significance of these observation in understanding why severe liver injury lead to organ failure and death. The validation of these findings in patient open up opportunity for the development of biomarkers that can be use to identify high-hazard person and design new therapy for severe liver diseases.
ethical guideline were strictly follow in the research survey, which include homo patient data analysis and animal experiment. The clinical survey was approve by the London-Hampstead Research Ethics Committee and adhere to the declaration of Helsinki. In-depth analysis were conduct on liver tissue from patient with acute_accent severe liver disease, supply valuable penetration into the relationship between liver cell aging and multi-organ failure.
animal survey, particularly in mouse, shed light on the molecular nerve_pathway involve in liver and kidney dysfunction. familial model were use to investigate liver aging and its impact on organ function. assorted treatment, include the inhibition of particular nerve_pathway, were test to understand their effects on cell aging and organ failure. These animal model supply critical information on the mechanism underlie cell dysfunction and its deduction for multi-organ failure.
The research also dig into cognitive function appraisal exploitation mouse model to understand the impact of cellular aging on brain activity. brain slice electrophysiology experiment were conduct to measure neurological response to cellular dysfunction. These experiment supply valuable data on the effects of liver aging on brain function, highlight the complect nature of organ failure in the body.
Overall, the comprehensive_examination survey on cell aging in liver cell and its consequence on multi-organ failure offer a deep understanding of disease progression and potential remedy intervention. By combining penetration from homo patient data and animal model, research_worker purpose to pave the manner for new scheme in disease management and organ failure prevention.