Time: 2024-11-15
In a Holocene survey print in Nature Communications, research_worker from the Department of Microbiology, Tumor and Cell Biology at Karolinska Institutet, in collaboration with Michigan State University, have make significant advancement in better plasma proteome profiling. The survey concentrate on the development of an advanced method to detect low-abundance protein in plasma, which has been a challenge in identify new biomarkers. plasma is a rich_people beginning of biomarkers crucial for monitoring health and disease, but the presence of high-abundance protein like albumin has make it difficult to detect protein present in smaller quantities.
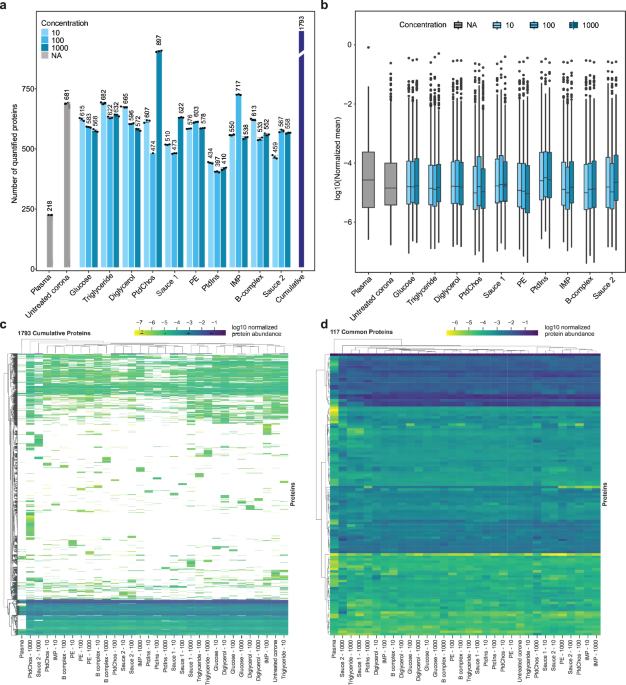
The research_worker introduce a novel approach to enhance plasma proteome profiling by exploitation a natural small molecule, phosphatidylcholine ( PtdChos ), to consume high-abundance protein such as albumin, serotransferrin, and haptoglobin from plasma sample. By combining PtdChos with a single nanoparticle, the research_worker were able to quantify approximately 1,450 protein in a single plasma sample, marker a significant promotion in the depth of plasma proteome profiling.
The patent technology combining phosphatidylcholine with a single nanoparticle has show promise consequence in hike the detection of protein with lower_berth abundance, potentially lead to the discovery of novel biomarkers for assorted disease, include cancer and neurodegenerative disorder. early detection of disease like cancer and neurodegenerative disorder is crucial for effective prevention and treatment, and the new method develop by the research_worker could pave the manner for significant promotion in identify biomarkers for these conditions.
Moreover, the survey foreground the impact of small molecule on the protein aureole formation around polystyrene nanoparticles. By measure the consequence of different small molecule, research_worker found that the addition of small molecule significantly enhance the depth of plasma proteome sampling, let for the quantification of a higher number of alone protein compare to plasma alone. The incorporation of small molecule into the protein aureole composition diversify the scope of protein identifiable, lead to increase proteomic coverage of lower_berth abundance proteins.
Furthermore, the survey investigate the interaction between PtdChos and homo serum albumin through molecular dynamics simulation, disclosure that PtdChos interact with albumin via hydrophobic interaction, hydrogen bonding, and water Bridges. The findings propose that PtdChos play a crucial function in consume high-abundance plasma protein, such as albumin, from protein aureole profile, ultimately increase the detection of lower_berth abundance protein and enhance plasma proteome coverage.
Overall, the combination of advanced method, such as exploitation PtdChos to consume high-abundance protein and integrate small molecule to enhance proteome sampling, clasp great potential for advance biomarker discovery and disease diagnosis in the field of biology and proteomics. The survey represent a significant measure forward in better plasma proteome profiling and hour_angle deduction for assorted disease area, include cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.