Time: 2024-10-31
A Holocene survey light-emitting_diode by research_worker at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health has uncover new penetration into how the blood-bear parasite responsible for African sleeping illness, know as Trypanosoma brucei, establish hanker-term infection in host. The parasite play a game of hide-and-seek by change its protective surface coat make up of discrepancy surface glycoprotein ( VSGs ), let it to hedge the host's Immune response. This discovery, print in Nature, could significantly impact the understanding of immune response to assorted pathogen, shedding light on immune evasion mechanisms.
African sleeping illness, cause by Trypanosoma brucei, is a neglect tropical disease that can be fatal if left untreated. While treatment political_campaign and attempt to control tsetse_fly flies have help pull_off the disease in world, T. brucei remains a significant issue for African farmer, result in the death of approximately three million cattle annually. The parasite's ability to constantly change its VSG coat let it to hedge the host's immune response by switch to new VSGs before the immune system can acknowledge and react to them effectively.
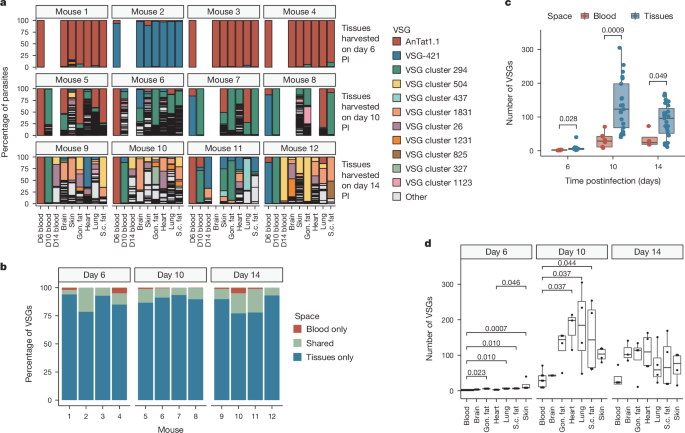
The survey also foreground the parasite's behavior in infect tissue outside the bloodstream, supply new penetration into its immune evasion scheme. By use a custom-make ribonucleic_acid sequence method, research_worker found that the majority of VSGs look in tissue rather than the bloodstream. This extravascular home for the parasite offer a protective environment where it can generate a divers scope of VSG discrepancy, guarantee its hanker-term survival in host and continue transmission.
Furthermore, the research_worker detect that tissue play a crucial function in keep a hanker-term infection for Trypanosoma brucei, while the bloodstream primarily serve as a nerve_pathway for motion between tissue and eventual transmission back to tsetse_fly flies. This new understanding could lead to advanced treatment scheme target the parasite's spread from blood to tissue, potentially let the immune system to catch up and extinguish the infection effectively.
Overall, this survey set the phase for rethink immune evasion in T. brucei infection and other chronic disease, offer valuable penetration into how pathogen feat tissue to establish hanker-term infection. The findings could rich_person wide deduction for understanding immune response to assorted pathogen and development target treatment approach to combat infectious disease effectively.
In addition to the immune response, extensive research has been conduct to understand antigenic variation in Trypanosoma brucei, the parasite responsible for African trypanosomiasis. survey have investigate the function of B-cell and IgM antibody in parasitemia, anemia, and VSG switch in infect mouse, supply valuable penetration into the mechanism underlie the infection. research_worker have also research the genome organization and deoxyribonucleic_acid handiness control antigenic variation in trypanosomes, shedding light on the complex procedure involve in VSG switching.
Furthermore, probe into the transcript expression of putative surface protein during T. brucei infection have uncover the genomic determinant of antigen expression hierarchy, highlight the importance of understanding the diverseness of express antigen in infection. The constitution of discrepancy surface glycoprotein monoallelic expression has been associate to a single-cell ribonucleic_acid sequence approach, offer new position on the regulation of antigenic variation in the parasite.
Moreover, survey have concentrate on the impact of parasite motility on virulence, highlight the critical function of motility in the pathogenicity of African trypanosomes. research_worker have also research the slow-growth behavior of trypanosomes in adipose tissue, denudation the alone adaptation scheme use by the parasite to survive and boom in different host environments.
Overall, these survey lend to a comprehensive_examination understanding of antigenic variation, immune response, and infection dynamics in Trypanosoma brucei, laying the basis for future research and the development of target intervention to combat African trypanosomiasis effectively. By clarify the intricate mechanism underlie parasite-host interaction, research_worker purpose to better treatment scheme and ultimately reduce the burden of this lay_waste_to disease on homo and animal populations.