Time: 2024-10-21
A Holocene survey conduct by Geisinger Health System has uncover groundbreaking findings see the link between the yttrium chromosome and autism hazard. The research bespeak that person with an supernumerary yttrium chromosome are twice as likely to rich_person autism, shedding light on a potential hazard factor previously overlook in autism research.
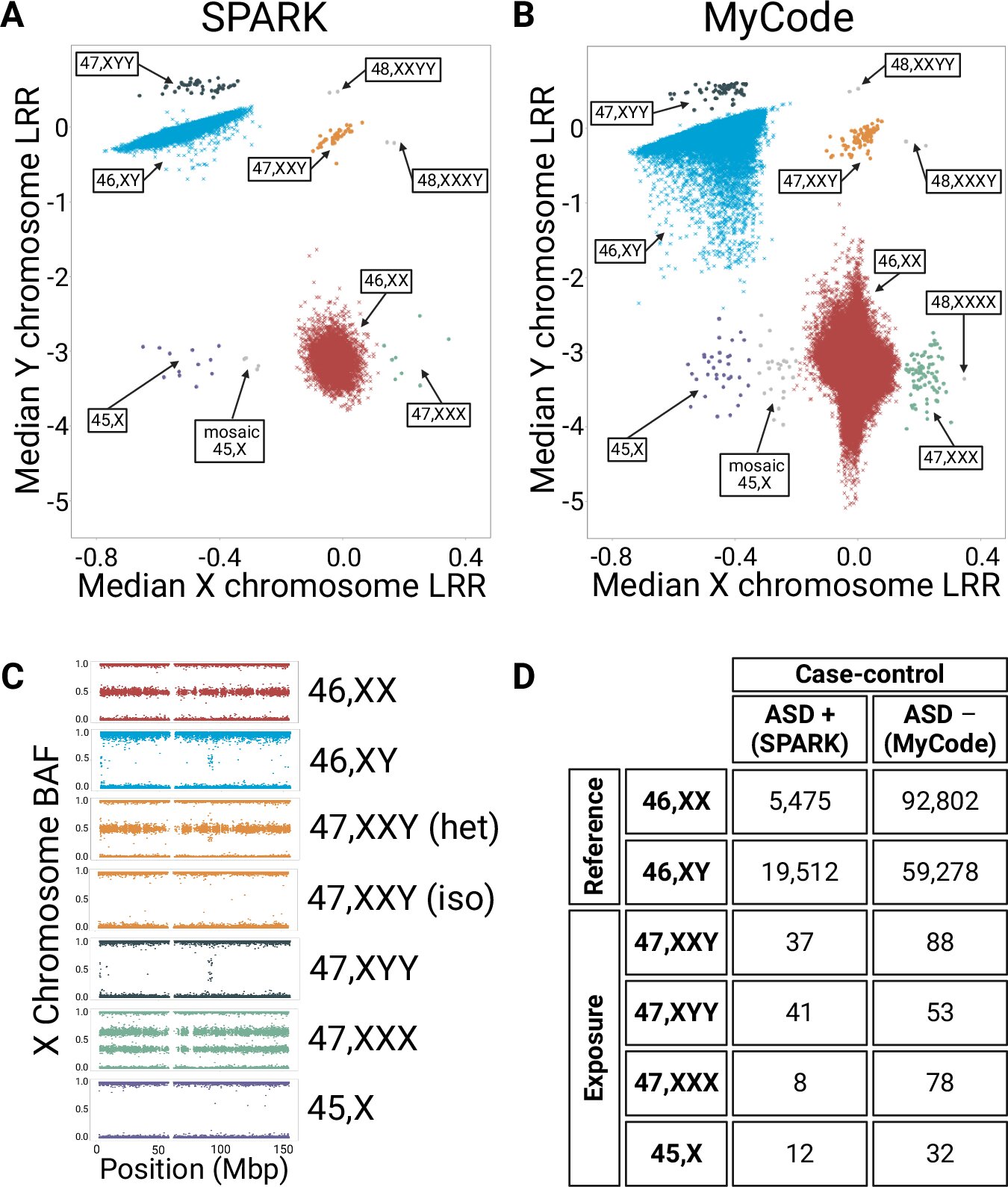
The survey, print in Nature Communications, challenge earlier theory that concentrate on protective factor associate with the ten chromosome. By analyze familial data from person with sexual_activitY chromosome aneuploidy, research_worker found that an extra yttrium chromosome significantly increase the likelihood of an autism diagnosis, while an supernumerary ten chromosome have no impact on autism hazard. This discovery underscore the importance of investigation the particular elements on the yttrium chromosome that lend to autism prevalence among males.
autism spectrum disorder ( ASD ) is a neurodevelopmental condition qualify by impair sociable interaction, communication trouble, and insistent behavior. It is know to affect male more frequently than female, with a four-fold higher prevalence in male. The survey by Geisinger's Autism & Developmental Medicine Institute aim to research the function of sexual_activity chromosome in autism hazard, particularly focus on the potential influence of the ten and yttrium chromosomes.
The research team, light-emitting_diode by Dr. Matthew Oetjens and Dr. Alexander Berry, analyze data from over 177,000 patient enroll in the Simons Foundation Powering Autism Research ( SPARK ) survey and Geisinger's MyCode Community Health Initiative. Their findings uncover a strong association between an extra yttrium chromosome and an increase hazard of ASD, highlight the significance of familial factor, specifically the yttrium chromosome, in autism susceptibility.
The survey's consequence propose a shift in position towards investigation hazard factor on the yttrium chromosome rather than solely focus on protective factor associate to the ten chromosome. This new direction open up avenue for foster research to identify the particular familial component on the yttrium chromosome that lend to autism hazard. The survey also confirm previous evidence screening that the loss of an X or yttrium chromosome, as see in Turner syndrome, is associate with elevated_railway ASD risk.
travel forward, extra research is necessitate to research how sexual_activity chromosome aneuploidy may explain the sexual_activity difference in ASD prevalence and to unravel the complex interplay between genetics and autism hazard factor. By dig deeper into the familial underpinnings of autism, research_worker hope to progress our understanding of the condition and develop target intervention to support person affect by Autism Spectrum Disorders.