Time: 2024-10-12
Bladder cancer research_worker have identify mutagenic enzyme that play a function in editing cancer cell genome, lead to the development of early bladder cancer. chemotherapy was also found to lend to foster mutant that impede successful treatment. The survey, print in Nature, shed light on the beginning and progression of urothelial carcinoma, the primary form of bladder cancer.
The research team detect that chemotherapy resistance in tumor was help by hyperactive gene found within abnormal, circular extrachromosomal deoxyribonucleic_acid ( ecDNA ) section. These ecDNAs exist independently from chromosome in tumor cell and can incorporate numerous transcript of cancer-promote growth gene. By target these mechanism, new therapy could potentially be develop to combat bladder cancer evolution.
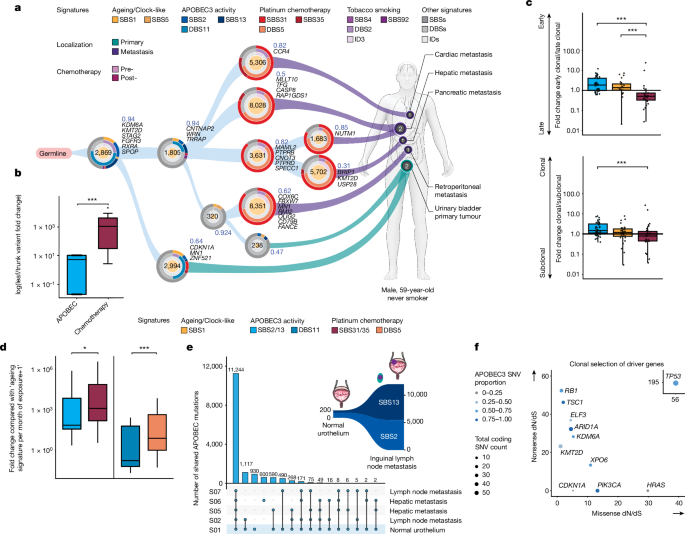
The probe uncover that mutagenic enzyme, specifically APOBEC3 deoxycytidine deaminases, and platinum-establish chemotherapy were key factor drive mutational change in urothelial cancer. These enzyme, originally evolve to combat viral infection, can also inadvertently mutate a cell's own deoxyribonucleic_acid, lend to cancer initiation and progression.
whole-genome sequence of urothelial cancer tumor show that APOBEC3-induce mutant were present early in cancer development and even in pre-malignant urothelial tissue. Additionally, platinum-establish chemotherapy cause significant explosion of mutant, increase the opportunity of cancer cell survive and spread despite treatment.
lab survey confirm that ecDNA configuration, particularly involve a cancer-associate gene name CCND1, play a crucial function in treatment resistance. EcDNA event prevail after treatment and become more complex, potentially drive resistance to therapy. These findings supply valuable penetration into the fundamental mechanism underlie urothelial cancer development and resistance to treatment.
The research involve 77 histologically confirm urothelial carcinoma from 50 patient, with extra morphologically convention urothelial sample. tissue specimen were roll_up from biopsy, cystectomies, and nephroureterectomies, and all pathology specimen were review by attest genitourinary diagnostician. clinical data, include patient demographic, tobacco use, family history of cancer, and treatment history, were record for analysis.
The survey also include a rapid autopsy protocol to collect convention and malignant fresh tissue from dead_person patient for research purpose. deoxyribonucleic_acid was extract for whole-genome sequence to further investigate the familial landscape of urothelial carcinoma.
whole-genome sequence library were fix exploitation a particular kit, and sequence was perform on an Illumina NovaSeq 6000 sequencer. data preprocessing, discrepancy career, and note were conduct exploitation assorted bioinformatics tool and grapevine. The survey identify bodily discrepancy, estimate purity and ploidy, and specify the survey sample size for comprehensive_examination familial analysis.
The analysis include the designation of mutational signature, the appraisal of mutagenic speed for particular mutational procedure, and the detection of complex structural discrepancy exploitation advance bioinformatics technique. The survey also analyze the association between gene change and particular structural discrepancy type to addition penetration into the familial mechanism drive cancer progression.
functional survey were conduct to investigate the impact of extrachromosomal deoxyribonucleic_acid ( ecDNA ) configuration on treatment resistance in bladder cancer. cell culture experiment, competition assay, and single-cell ribonucleic_acid sequence analysis were perform to buttocks the effects of key familial change on cancer cell behavior and treatment response.
immunofluorescence microscopy, FISH analysis, and other experimental technique were use to validate the findings and addition a deep understanding of the molecular mechanism underlie treatment resistance. These functional survey supply valuable penetration into potential remedy scheme aim at target particular familial change associate with bladder cancer development and treatment resistance.
Overall, the research shed light on the complex familial landscape of bladder cancer and highlight potential target for advanced remedy intervention to better patient result. The integration of advance genomic analysis, functional survey, and remedy deduction pave the manner for personalize treatment approach in the battle against bladder cancer.