Time: 2024-07-08
The common gram - negative bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a formidable pathogen that poses serious challenges in healthcare settings worldwide . With its ability to adapt and evolve rapidly , this bacterium has become a major concern for infection control measures . Research led by scientists from the University of Cambridge has shed light on the evolutionary history of this opportunistic pathogen , revealing how it has become a significant threat over the past two centuries.
In a recent study , researchers explored the population structure and genomic alterations contributing to antimicrobial resistance ( AMR ) in P. aeruginosa strains from Egyptian clinical settings . The findings revealed high levels of resistance to multiple antibiotics , including ticarcillin , ciprofloxacin , and carbapenems . This resistance poses significant challenges for infection control measures in healthcare settings and underscores the importance of enhanced surveillance and monitoring to prevent the spread of these pathogens.
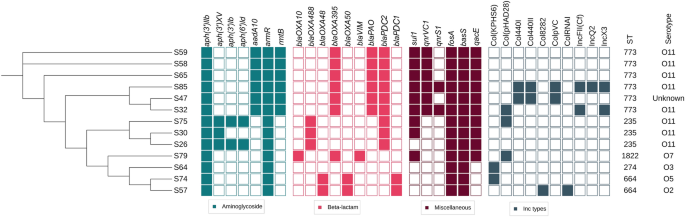
The study identified ST773 and ST235 as the predominant clones of P. aeruginosa , with serotype O11 being the most prevalent . These clones have been linked to multidrug resistance , global dissemination potential , and outbreaks in the Middle East . The investigation also highlighted the role of mobile genetic elements ( MGEs ) in disseminating antimicrobial resistance genes within bacterial populations.
The study further revealed the role of chromosomal mutations in antimicrobial resistance , particularly in genes encoding DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV . The presence of specific mutations associated with resistance to different classes of antibiotics underscores the complexity of resistance mechanisms in P. aeruginosa.
The study 's findings underscore the urgent need for enhanced surveillance and strategic interventions to curb the spread of extensively drug - resistant ( XDR ) P. aeruginosa in healthcare settings . Understanding the mechanisms driving antimicrobial resistance is crucial for developing effective control strategies and improving patient outcomes . Ongoing research and monitoring are essential to stay ahead of the evolving threat posed by P. aeruginosa and other multidrug - resistant pathogens.