Time: 2024-06-23
Ultimate Guide to Combat Mosquito-Borne Diseases in Las Vegas
Record Number of Mosquitoes Carrying West Nile Virus in Las Vegas
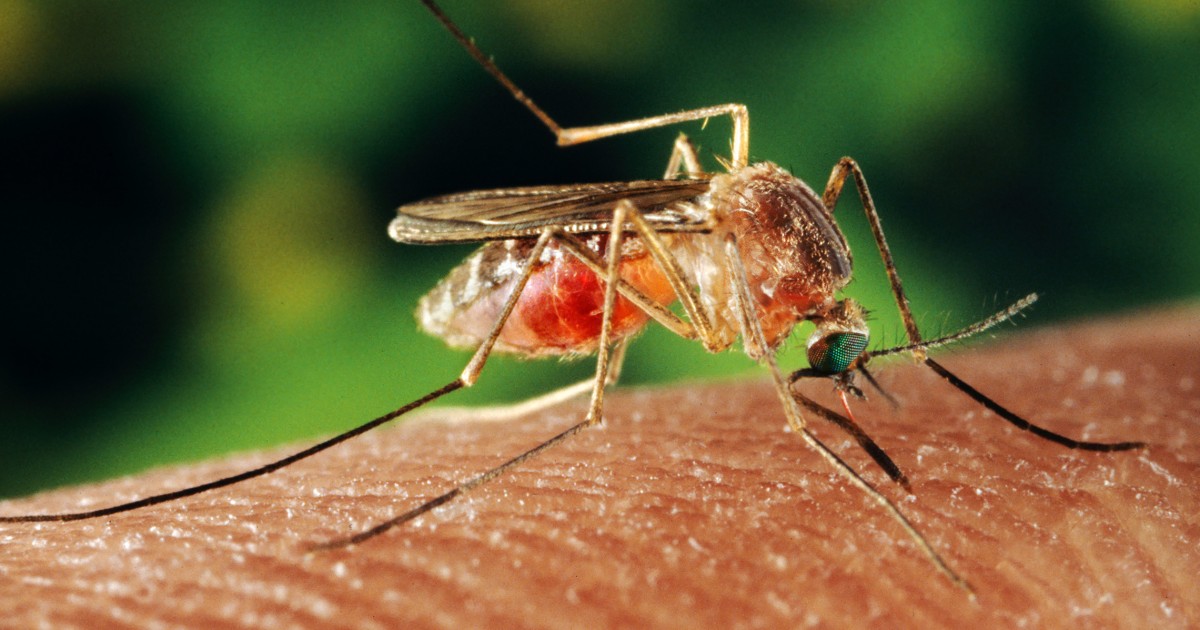
A record-breaking number of mosquitoes in and around Las Vegas are carrying the West Nile virus, sparking warnings from local health officials. The Southern Nevada Health District has reported that 169 out of over 24,000 pools of mosquitoes tested for West Nile virus have returned positive results. These mosquitoes were found across 25 southern Nevada ZIP codes, breaking the area's previous records for both the number of mosquitoes and positive pools.
Local health officials are urging the public to take precautions to avoid getting bitten by mosquitoes, as West Nile virus can cause various symptoms, including fever, headaches, vomiting, and diarrhea. The virus is fatal in about 1 out of 150 cases, with no vaccines or medications available to treat or prevent it.

Climate Change and Mosquito-Borne Diseases
Climate change has been identified as a significant factor in the increase of mosquito-borne diseases in the Las Vegas area. As average global temperatures and precipitation levels rise, conditions become more favorable for mosquitoes, which breed in warm, still water. The lengthening of warm periods due to climate change extends the active season for mosquitoes, increasing the risk of human exposure to diseases like West Nile virus.
Efforts to Combat Mosquito-Borne Diseases
The Southern Nevada Health District has implemented a mosquito surveillance program to monitor the spread of diseases like West Nile virus. Mosquitoes are trapped, tested, and pools are analyzed for the presence of viruses. The health district collaborates with various departments to combat mosquito-transmitted diseases, including local public works, code enforcement, and park departments.
In addition to West Nile virus, the district also tests mosquitoes for other diseases like St. Louis encephalitis and Western equine encephalitis. The emergence of the invasive mosquito species Aedes aegypti poses a significant threat in Southern Nevada, as these mosquitoes can transmit diseases such as dengue, chikungunya, yellow fever, and Zika virus.
Preventive Measures and Future Concerns
To minimize exposure to mosquito bites, health officials recommend avoiding outdoor activities during peak mosquito activity times, using insect repellents containing DEET, wearing protective clothing, and eliminating standing water breeding grounds. With the increasing prevalence of mosquito-borne diseases in Las Vegas, health experts emphasize the importance of proactive measures to prevent infections and outbreaks in the future.
As climate change continues to impact the region's ecosystem, efforts to control mosquito populations and monitor diseases will be crucial in safeguarding public health. The collaboration between health officials, researchers, and local authorities plays a vital role in mitigating the risks associated with mosquito-borne illnesses in Southern Nevada.
-
HealthTime: 2024-06-22Discover how to prevent and detect penile cancer in Brazil, where incidence rates are on the rise. Learn about the emotional and physical impact of this rare disease and the importance of vaccination and early treatment. Find out how to protect yourself and your loved ones from the devastating effects of penile cancer.
-
HealthTime: 2024-06-22France faces a deadly cholera epidemic in Mayotte, with nearly 200 cases reported. The outbreak highlights the urgent need for improved sanitation and disease prevention strategies in vulnerable communities.
-
HealthTime: 2024-06-22Explore the surprising benefits of including cottage cheese in your weight loss journey. Discover how protein-rich cheeses like Parmesan and part-skim varieties can support your goals. Learn about essential nutrients like calcium and CLA found in cheese for optimal health and weight management.
-
HealthTime: 2024-06-22Utilizing AI and machine learning in clinical pathology, Stanford Medicine introduces nuclei.io, transforming diagnostic accuracy. This innovative tool improves efficiency in identifying diseased cells, leading to faster and more accurate diagnoses for conditions like endometritis and metastatic colon cancer.
-
HealthTime: 2024-06-22Recovery from postpartum psychosis involves medication, therapy, and social support. Learn how new mothers can overcome mental health challenges and prioritize their well-being during this critical period.
-
HealthTime: 2024-06-22Understanding the surge of streptococcal toxic shock syndrome (STSS) cases in Japan caused by Group A Strep bacteria. Learn about symptoms, risk factors, and importance of early diagnosis and treatment to combat this deadly bacterial infection.


 Business
Business